Sleep Apnea vs. Snoring: What’s the Difference?
Introduction
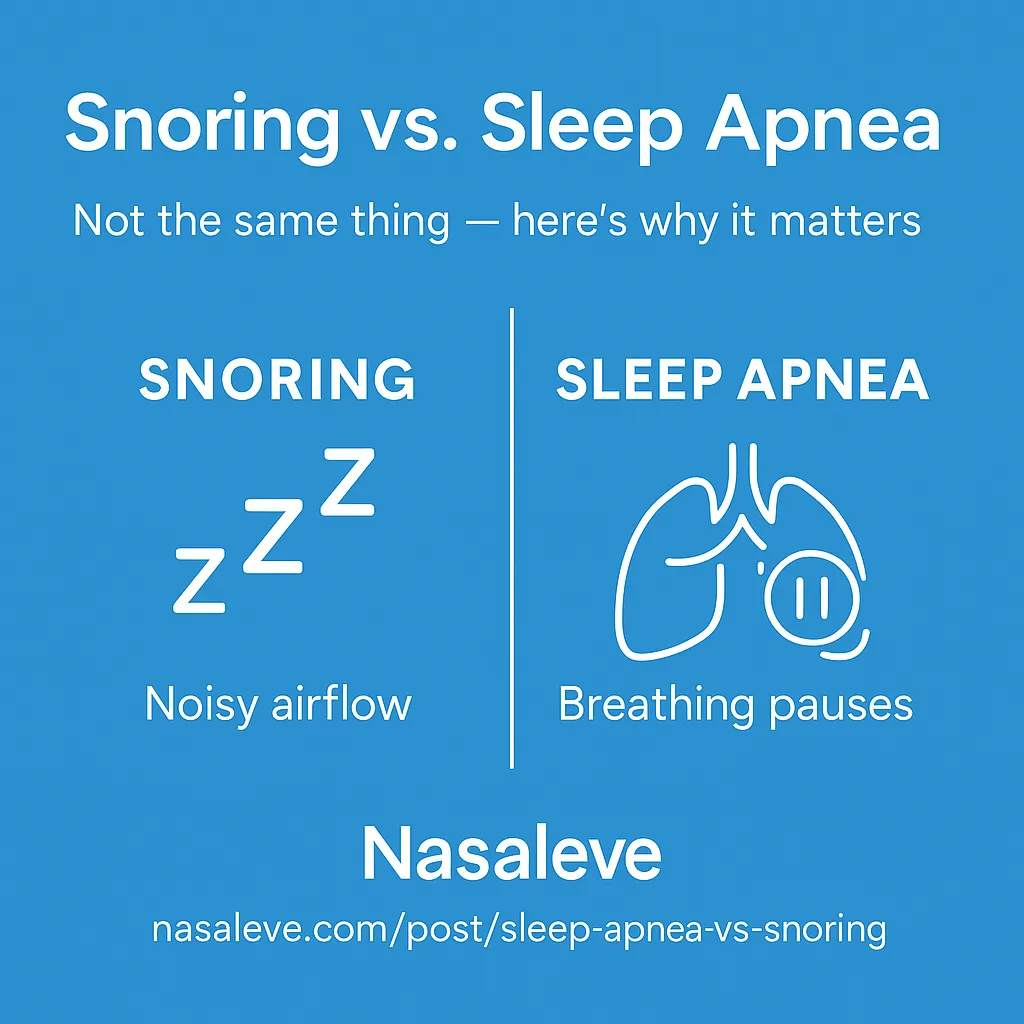
Snoring is common — but when does it cross the line into something more serious like sleep apnea? While both involve disrupted breathing during sleep, they’re not the same. Understanding the difference can help you know when simple fixes might work — and when it’s time to seek medical help.
What Is Snoring?
Snoring happens when airflow is partially blocked, causing tissues in the nose, mouth, or throat to vibrate.
Often linked to mouth breathing, congestion, or internal nasal valve collapse
Usually disruptive to bed partners but not always dangerous
May be occasional or nightly, depending on underlying causes
Snoring is a symptom, not a condition on its own.
What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea, specifically obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), is a disorder where the airway repeatedly narrows or closes entirely during sleep.
Breathing pauses can last 10+ seconds
Oxygen levels drop, forcing the body to wake partially to resume breathing
Symptoms include gasping, choking, daytime fatigue, and poor concentration
Sleep apnea is more than snoring — it’s a medical condition with serious health risks.
Key Differences Between Snoring and Sleep Apnea
Severity
Snoring = noisy airflow
Sleep apnea = actual pauses in breathing
Health Impact
Snoring = inconvenience, lighter sleep
Sleep apnea = linked to heart disease, high blood pressure, and more
Daytime Symptoms
Snoring = partner complaints, mild tiredness
Sleep apnea = extreme fatigue, brain fog, morning headaches
Treatment Needs
Snoring = may improve with lifestyle changes or nasal breathing aids
Sleep apnea = may require CPAP, oral appliances, or medical supervision
Why the Nose Plays a Key Role
Many cases of snoring — and even some mild apnea — start with restricted nasal airflow. When the internal nasal valve collapses inward, the body shifts to mouth breathing. This increases turbulence and makes snoring more likely.
By improving nasal airflow, some people can reduce snoring intensity and even decrease mild apnea symptoms.
Solutions to Consider
For Snoring:
Nasal breathing aids (like Nasaleve)
Lifestyle adjustments (weight, alcohol, sleep position)
Treating congestion or allergies
For Sleep Apnea:
CPAP therapy
Oral appliances
Surgery (in select cases)
Professional diagnosis is essential
Where Nasaleve Fits In
Nasaleve isn’t a medical treatment for sleep apnea — but it can play a big role in snoring relief. By supporting the internal nasal valve laterally, Nasaleve keeps airflow open at the narrowest point of the nose.
This helps reduce mouth breathing and snoring — improving sleep quality for both you and your partner.
Final Thoughts
Snoring and sleep apnea may sound similar, but the stakes are very different. Snoring is often a nuisance; sleep apnea can be a serious health condition.
If you’re unsure which you’re dealing with, talk to a healthcare provider. But if your main struggle is noisy, airflow-related snoring, restoring nasal breathing may be the simple, natural fix you’ve been looking for.
Call to Action:
👉 Learn more about natural snoring relief and how Nasaleve supports healthy airflow.